Fleet Management Software: Features and Benefits Explained
What is Fleet Management Software?
Definition and Scope
FMS, or Fleet Management Software, is one of the digital solutions and an example of custom software solutions designed to streamline fleet operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall efficiency. Its core functionalities include tracking of vehicles, route optimization, maintenance scheduling, monitoring of fuel consumption, behavior analysis of drivers, and compliance reporting.
The components of FMS are well integrated with existing business workflows and allow for real-time access and analytics that drive decision-making. This is widely applied in a wide variety of fields, ranging from logistics and delivery companies to ride-hailing companies to public transportation and service-based businesses with large vehicle fleets.
Main Goals of Fleet Management Software:
Reducing Costs: To help you minimize fuel wastage, maintenance costs, and administrative overhead.
Improving Efficiency: Improve routes, minimize downtime, and improve overall productivity.
Enhancing Safety: Track driver behavior and vehicle compliance to safety standards.
Ensuring Compliance: EHS policies include Hours of Service (HOS) and emissions standards.
How it Works
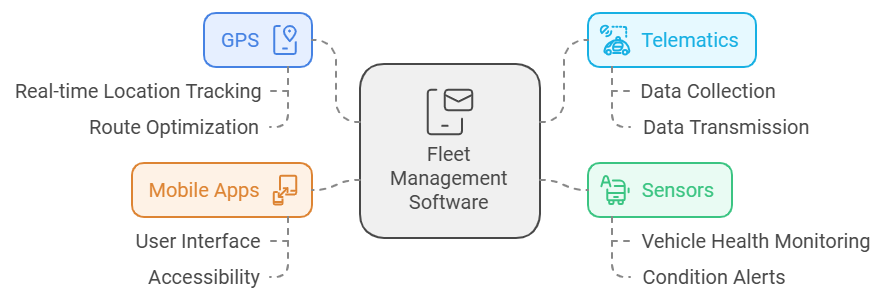
Fleet management software operates through a combination of cutting-edge technologies, ensuring efficient and real-time operations.
GPS and Telematics Solutions: It helps you to enable real-time vehicle tracking, optimize routes, and geofencing.
Sensors and IoT Devices: Monitor vehicle health, fuel consumption, and a driver’s performance.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing solutions are integral to fleet management, offering scalability and accessibility.
Mobile Apps and Dashboards: It allows on-the-go access to critical insights, alerts, and updates to provide fleet managers and drivers with.
Combining the three technologies together guarantees that businesses can make decisions based on data while keeping visibility and control of their fleets.
Purpose of Fleet Management Software
Fleet Management Software optimizes critical operational tasks, making fleet management more efficient and cost-effective.
Route Planning: This way will offer the best way to reduce travel time and fuel consumption.
Vehicle Tracking: With real time visibility of vehicle locations, this serves as a performance accountability tool to the customer.
Fuel Management: It monitors, and studies the pattern, to cut costs.
Compliance Monitoring: No fines, no penalties for guarantee vehicles.
Target Audience
Fleet Management Software serves a diverse range of businesses and organizations:
Logistics Companies: Simplify cargo movement and delivery schedules.
Delivery Services: Deliver on time, and optimize routes.
Public Transportation Agencies: Improve bus fleet service reliability.
Construction Firms: Basecamp allows you to monitor heavy equipment and vehicles on job sites.
Service-Based Businesses: Operations for fleets such as plumbing, HVAC, or electrical service.
Use Case Example
Real-World Scenario:
A leading EU-based logistics company serving over 500 businesses faced challenges in optimizing logistics operations and minimizing manual errors. By implementing a custom fleet management system integrated with real-time GPS vehicle tracking, the company achieved:
A 28% increase in fleet productivity through real-time monitoring and task automation.
Streamlined workflows that led to faster response times and improved operational efficiency.
Enhanced customer interactions via integrated portals and instant messaging features.
The transition resulted in significant cost savings and improved supply chain visibility, demonstrating the tangible benefits of the fleet management system implementation.
(Source: CleverDev Software)
Types of Fleet Management Software Solutions
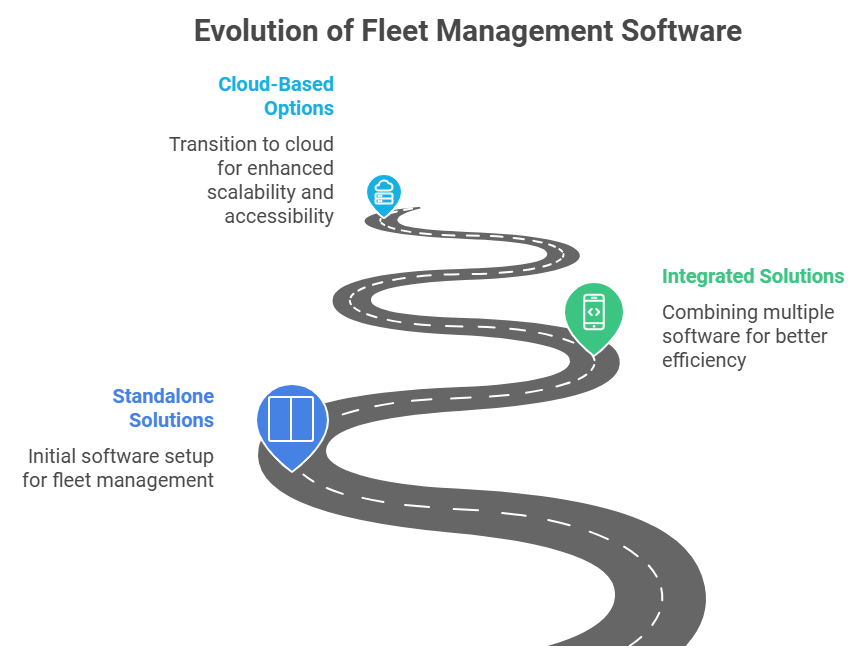
Standalone Fleet Management Software
Definition:
Standalone Fleet Management Software (FMS) focuses on a single aspect of fleet management. These solutions are designed to address specific operational needs, such as GPS tracking, fuel management, or driver behavior monitoring.
Key Features:
GPS Tracking: GPS Tracking provides real-time vehicle locations, facilitating route optimization and accountability.
Fuel Management: It tracks fuel consumption, identifies inefficiencies, reduces costs, and lessens fuel theft.
Driver Behavior Monitoring: Allows monitors to track speeding, hard braking and idling, touting safety and fuel efficiency.
Benefits:
It is designed to serve one core function for businesses.
Fewer upfront costs with everything reduced to basics.
Fueled capabilities that are easier to deploy and manage.
Limitations:
Isolated data — does not integrate well with other systems.
Consuming lots of time and resources is highly unlikely to scale well and may even miss the marks for business as the business itself evolves.
Example Use Case:
A small delivery company needing route optimization might use standalone GPS tracking software. It helps cut fuel costs and improve delivery timelines without requiring additional functionalities.
Integrated Fleet Management Software
Definition: FMS stands for ‘flee management system’ and combines multiple fleet management features into one comprehensive platform. This ties together a bunch of tools like route planning, vehicle health monitoring, driver performance tracking and fuel management and presents a holistic view of all fleet operations.
Key Features:
Comprehensive Fleet Tracking: Route optimization, real time GPS tracking and asset tracking.
Vehicle Maintenance Scheduling: Routine maintenance task alerts like oil change, tire rotation and brake check, all automated.
Driver Behavior Analysis: A wealth of driving habits and performance in-depth reports offering feedback for safer and more efficient driving.
Fuel Management and Analytics: Real-time monitoring of fuel usage to locate inefficiencies and reduce fuel costs.
Compliance Management: It helps you to track the information regarding regulatory requirements like hour of service (HOS), driver license and other inspection schedules.
Benefits:
They are all in one solution to simplify fleet operations by having a centralized platform.
It is scalable so that businesses can add or remove features as needed.
Improve decision-making with real time data across all fleet operations.
Limitations:
The breadth of features means a higher cost upfront compared to standalone software.
Often, they are complex to implement, especially when integrating with existing systems.
Example Use Case:
A logistics company with a large fleet needs to manage multiple aspects of operations, including route planning, maintenance schedules, driver behavior, and compliance management. An integrated fleet management system would be ideal for streamlining all of these processes into a single platform.
According to source LocoNav, Integrated Fleet Management Systems (IFMS) consolidate various functionalities such as GPS tracking, maintenance scheduling, and driver management into one comprehensive solution. This integration enhances operational efficiency by providing real-time insights and analytics, enabling logistics companies to optimize routes and improve compliance with industry regulations.
Cloud-Based Fleet Management Software
Definition: FMS on the cloud stores its data on remote servers that can be accessed over the internet. This kind of software works by removing the need for on-site servers or IT infrastructure and enabling fleet managers and drivers to access data anytime and from anywhere using an internet connection.
Key Features:
Real-Time Data Access: Available on any connected device – be that a smartphone, tablet, or laptop.
Remote Monitoring: The ability to monitor vehicles and observe the driver in real-time, even from a distance from the office.
Automatic Software Updates: Cloud systems automatically update, ensuring that the latest features and security patches are available.
Scalability: It is easily scalable and doesn’t require hardware or infrastructure to grow.
Benefits:
Lower overhead costs due to dependency on no internal IT support or infrastructure.
Authorized users can access the data from any place, which improves flexibility and operational agility.
A subscription-based pricing model that reduces the upfront cost.
Automatic backups and cloud disaster recovery minimize the risk of data loss.
Limitations:
Access to data is dependent upon a stable internet connection.
Costs over time that could become very high for larger fleets.
Example Use Case:
A field service company with employees working in multiple locations would benefit from a cloud-based Field Management System (FMS) because it allows for real-time monitoring of operations, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness across various sites.
Source Praxedo emphasizes that such systems provide critical features like GPS tracking and automated scheduling, which help streamline communication between technicians and dispatchers. This capability not only optimizes resource allocation but also improves customer satisfaction by ensuring timely service delivery and effective management of field operations.
On-Premises Fleet Management Software
Definition: FMS is installed on the company’s servers or hardware infrastructure thus on premises FMS. Large organizations, or those with specific security, compliance or customization needs, typically prefer this type of solution.
Key Features:
Customizability: Able to customize the software better to fit the company’s own specific fleet management needs.
Full Data Control: All the data of the fleet is stored and the management of them is in the hands of the business itself.
Integration with Existing Systems: Can be used in a company’s other software systems on site (HR, ERP systems).
Benefits:
Internal data control achieving enhanced security.
For specific fleet management needs or industry requirements, it is customizable.
Perfect for those companies that require a high degree of privacy or stringent data governance rules.
Limitations:
High upfront cost in hardware installation.
It calls for an entire IT team to maintain, update, and troubleshoot.
Unlike cloud-based, there is less flexibility due to data availability, both on-site and through VPN.
Example Use Case:
A multinational corporation with complex regulatory and data privacy needs may opt for on-premises fleet management software to maintain complete control over its data and ensure compliance with local laws.
According to source Fleetworthy, on-premises solutions provide enhanced security and customization, allowing organizations to tailor their systems to meet specific regulatory requirements while safeguarding sensitive information. This approach is particularly beneficial for companies operating across multiple jurisdictions, as it enables them to implement strict access controls and maintain comprehensive audit trails for compliance purposes.
Additionally, on-premises systems can be integrated with existing infrastructure, ensuring seamless operations and adherence to industry regulations.
Mobile Fleet Management Software
Definition: Mobile fleet management software is designed specifically to work with mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to enable operations to be managed using their fleet manager and drivers while on the go. It gives drivers a very easy-to-use interface for job details, submitting reports, and vehicle performance from their mobile devices.
Key Features:
Driver Communication: It enables drivers to directly use their mobile devices to receive real time updates, dispatches and communications.
Mobile Fleet Tracking: A mobile interface allows fleet managers to see where vehicles are located and how they are performing.
Real-Time Reporting: Drivers can update their status, write maintenance tickets, and report issues right from their mobile devices.
Electronic Logging Devices (ELD): Drivers’ hours of service can be tracked on mobile apps and, by legal regulations, can be compiled.
Benefits:
It helps increase communication efficiency between drivers and fleet managers.
It streamlines data collection and reporting, taking work off your hands and getting reports organized.
It reduces the time delay between the events to be reported and their reporting accuracy thus mostly improves the accuracy of real time information.
Limitations:
Reliant on mobile network coverage, which can be patchy in remote areas.
Drivers who need to become more familiar with mobile apps for fleet management may need further training.
Example Use Case:
A last-mile delivery company that needs to keep drivers informed and collect delivery status updates in real time can leverage mobile fleet management software to enhance communication and operational efficiency.
Source FarEye highlights that such software provides features like real-time tracking and automated scheduling, which help businesses stay proactive and ensure that customers are kept informed throughout the delivery process.
By utilizing a mobile platform, drivers can easily update delivery statuses, leading to improved transparency and customer satisfaction. This integration of technology ultimately streamlines operations and enhances the overall delivery experience.
Source Trackunit notes that such software simplifies the management of mixed fleets across various job sites, providing real-time insights into equipment utilization and maintenance needs.
This ensures compliance with industry regulations and enhances operational efficiency by reducing downtime and improving resource allocation.
Who Benefits the Most from FMS?
Logistics and Delivery Companies
Logistics Software Solutions (i.e. FMS) allows us to plan routes efficiently, track vehicles, and make deliveries timely and to lower operational costs.
How FMS Helps:
Real-Time Tracking and Route Optimization: Real-time tracking in logistics allows delivery companies to track vehicles and route them meaningfully, requiring less delivery time and use of fuel.
Timely Deliveries: FMS delivers accurate ETA tracking and traffic alerts to ensure that drivers arrive on time, thus increasing customer satisfaction.
Fleet Efficiency: Using FMS helps to plan a fleet of vehicles, trucks, vans to drones, to get the right vehicle produced at the right time, reduces downtime and optimize vehicle usage.
Why They Benefit:
- However, logistics companies operate large fleets with very strict time sensitive schedules. Minimizing operational costs calls for efficient route planning, and also maintenance management.
Public Transportation Providers
By ensuring route optimization, accurate time tracking, and safety compliance for buses and public transit fleets.
How FMS Helps:
Vehicle and Passenger Safety: This gives public transport companies the ability to track buses, trains, or trams in real time for better operations and smoother travel of passengers and to monitor and check driver behavior.
Route Planning and Optimization: FMS can optimize public transportation routes using real-time data to reduce both congestion and the amount of time trains take to get from point to point.
Compliance Management: This helps ensure meeting regulatory drivers’ working hours and vehicle emissions as per transport laws.
Why They Benefit:
- A large fleet of vehicles run on fixed schedules and are operated on public transport services. FMS is an efficient route planning, safety monitoring and industry regulation compliance tool in maintaining punctuality and safety.
Service-Based Industries (Plumbing, Electrical, HVAC, etc.)
FMS allows scheduling and dispatch to be better, thus keeping service calls timely and optimizing resource utilization.
How FMS Helps:
Scheduling and Dispatching: Quick response to a customer request is vital for service industries. Dispatch is stabilized on FMS by assigning the technician closest to a job based on real-time location data.
Improved Customer Experience: The speed of communication and tracking is more real time, which increases the amount of customer satisfaction.
Construction and Heavy Equipment Companies
It keeps data on where and how often the heavy machinery was used and where it is located.
How FMS Helps:
Asset and Equipment Management: In addition to tracking vehicles, FMS also ensures that heavy construction equipment is not stolen and that it’s available for your job when you need it.
Maintenance and Utilization: Heavy-duty vehicle usage, maintenance schedules, and condition reports can be tracked by the software and equipment life can be optimized in the process.
Why They Benefit:
- Large fleets of specialized vehicles and equipment are the norm for many construction companies and are often managed by tracking maintenance, fuel and asset security. FMS guarantees safe and efficient operation of high value assets.
Fleet Rental and Leasing Companies
With FMS, vehicle availability and reliability are increased to support the maintenance management and customer service aspects of asset tracking.
How FMS Helps:
Inventory Management: This allows fleet rental companies to know when their vehicles are available, how they are being used, and what condition the vehicles are in.
Billing and Usage Analytics: FMS takes care of the billing end, meaning how many miles you’ve driven or hours you used are tracked down, it streamlines the billing process for customers.
Why They Benefit:
- Large inventories of vehicles make fleet leasing companies susceptible to losing vehicles from old stock, without having the necessary vehicles available for clients. Real time monitoring, and maintenance scheduling, inventory management can all be achieved through FMS.
Food Delivery and Catering Services
It provides for fast, accurate, and efficient deliveries, optimized routing, and real time updates for drivers and customers.
How FMS Helps:
Temperature Monitoring: Reaching the right temperature is crucial for many food delivery businesses. Temperature sensors are integrated with FMS to ensure that correct transport conditions are maintained.
Compliance and Food Safety: It tracks when food was prepared and when it was delivered, helping ensure compliance with health and safety standards.
Why They Benefit:
- Time constraint and perishable goods are the common scenarios that food delivery catering services encounter, and there is the need for proper management of these issues. FMS will help make products quality through maintaining products, transportation of food safely, and delivery routes.
Waste Management Companies
FMS allows for route optimization for garbage collection and route and vehicle specialty tracking for route efficiencies.
How FMS Helps:
Route Optimization: There are vast volumes to pick up in both areas and there is little time to get it done, so you need efficiency. Waste collection routes are optimized by FMS to save time, and reduce fuel consumed.
Regulatory Compliance: Emits compliance verifies that all vehicles are compliant with local environmental and emissions regulations in order to avoid paying fines and penalties to companies.
Why They Benefit:
- Fleets of waste management companies are in continuous use, often on very tight schedules and with significant environmental regulations. FMS makes sure routes are optimized, vehicles are maintained, and they remain in compliance.
Oil, Gas, and Utility Companies
It enables safety compliance and ensures vehicle performance monitoring and field operations in remote areas.
How FMS Helps:
Vehicle and Asset Monitoring: Tallies utility and service vehicle use in maintenance, repairs, or installation. FMS assures that the right vehicle is available for the job.
Safety Monitoring: In high-risk industries like oil and gas, fleet management software tracks vehicle performance and driver behavior, ensuring safety standards are met.
Why They Benefit:
- In remote locations or under hazardous conditions, utility and energy companies operate fleets. The purpose of FMS is to streamline operations and make sure vehicles are tracked for safety, fuel efficiency, and other regulatory compliance.
Delivery and Courier Companies (Including E-commerce)
FMS helps to speed up the delivery, makes them more accurate, and reduces fuel costs — all for increased customer satisfaction.
How FMS Helps:
Route Optimization for Speedy Deliveries: Couriers can plan packages more rapidly and efficiently with route planning and real time traffic updates that improve customer satisfaction.
Inventory and Asset Tracking: It tracks delivery vehicles and packages so there is less risk of misplaced or lost items.
Why They Benefit:
- Many of these companies are squeezed into tight time frames and daily deliveries at a high volume. By improving route efficiency, customer service, and operational transparency, FMS makes a competitive advantage possible.
Car Dealerships and Fleet Operators
It helps with vehicle inventory tracking, maintenance planning, and performing value-added fleet services.
How FMS Helps:
Fleet Tracking and Monitoring: FMS is used by car dealerships and fleet operators to manage both sales cars and leased cars. They can monitor mileage, vehicle location, and vehicle health.
Depreciation and Maintenance Management: It helps track vehicle maintenance schedules to do proper care and increases resale value.
Why They Benefit:
- Vehicle maintenance schedules, customer communication, and overall fleet utilization can all be managed by dealerships with large fleets of vehicles for leasing or sales. Fleet management and transparency made FMS easier and simpler.
Core Features of Fleet Management Software: A Closer Look
GPS Tracking and Real-Time Vehicle Monitoring
Fleet managers will always be able to see in real time where the vehicles are located and thus make better decisions with greater operational efficiency.
What it Does: Offers real time tracking of vehicles with GPS technology to locate down to their exact position.
Benefits:
Improved route optimization
Fleet managers have real-time visibility
Route Optimization and Dynamic Routing
It works to identify the most efficient routes that reduce fuel consumption and deliver faster.
What it Does: It decides the best route for each trip using real-time traffic data, weather reports, and historical data.
Benefits:
Reduces time for drivers and customers.
To improve operational efficiency and good on-time performance
Vehicle Maintenance and Health Monitoring
Fleet management software tracks the health of vehicles, sending alerts for maintenance tasks, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and extending vehicle lifespan.
What it Does: It tracks vehicle performance and schedules automated maintenance tasks.
How it Works: Telematics can monitor engine health, tire pressure, oil levels, and other vital performance parameters in the software.
Benefits:
Maintenance done proactively avoids unpredictable breakdowns and costly repairs.
Helps to bring the fleet in line with safety regulations.
Driver Behavior Monitoring and Reporting
It monitors drivers’ speed, acceleration,n and braking behaviors, and provides insights that will lead to safer driving, and fuel-efficient practices.
What it Does: It monitors the important metrics of driver performance such as speed, braking pattern, acceleration and idle time.
How it Works: Driver behaviour is measured by telematics sensors which transmit the data back along to the fleet manager’s dashboard.
Benefits:
Real-time feedback with behavior correction for improved safety
Better habits in driving improve fuel efficiency.
Fuel Management and Consumption Tracking
It tracks fuel usage to help fleets run as efficiently as possible to identify inefficiencies and contribute to cost saving efforts.
What it Does: It monitors fuel usage across the fleet and analyzes patterns to detect inefficiencies or fraud.
How it Works: Integrates with fuel cards or direct fuel pump reports,and tracks fuel consumption at the vehicle level.
Benefits:
Identify fuel theft or misuse
Refueling schedule optimization and reduction in unused (unnecessary) fuel stops
Geofencing and Boundary Alerts
Geofencing technology is a form of boundary technology used to set virtual boundaries around a specific location and to alert if a vehicle goes into or out of a defined zone to increase security and operational control.
What it Does: It creates virtual geographic boundaries around defined locations and triggers alerts when vehicles are entering or leaving those zones.
Benefits:
Provides intelligence to managers who can decide if vehicles have left specified areas and escalate security as necessary.
It helps businesses set delivery and service area boundaries.
Compliance and Regulatory Management
The automation will help businesses stay compliant with legal and regulatory requirements, things like driver hours, inspections and licensing.
What it Does: Provides assurance that fleets are compliant with industry rules of, elements such as Hours of Service (HOS), emissions standards and safety inspections.
Benefits:
It reduces costly fines and penalties and also reduces risk.
Adheres to legal working hours limited, thus improving driver well-being.
Reporting and Analytics
Reports on fleet performance, driver behavior, maintenance schedules, and more provide data driven insight on how to make informed decisions and provide continuous improvement.
How it Works: Customizable dashboards and reports are provided by the software to help fleet managers track KPIs and find improvements.
Benefits:
It has the ability to identify a cost-saving opportunity.
Offers actionable knowledge to increase operational performance
Integration with Third-Party Tools
Fleet management software connects with third-party tools such as CRM or telematics systems to allow for a unified approach to streamlined fleet operations for better overall efficiency.
What it Does: Allows FMS to interface with other business systems, including CRM, ERP, or accounting software.
Benefits:
Reducing manual data entry along with improved workflow
Business data with higher accuracy and consistency
The Future of Fleet Management Software
The fleet management industry can be applied to that technology evolves to make smarter and more efficient fleet management possible. FMS will change many things with the advent of newer technologies such as AI, electric vehicles, and IoT. What will the future for FMS and these innovations look like? How will these innovations impact the industry?
AI and Machine Learning
Predictive Maintenance: FMS will predict when the vehicles need maintenance well before a breakdown using real-time data and historical patterns; that’s where AI will come into the picture. It will save businesses money in repair costs and downtime.
Route Optimization: Route planning will be continuously improving using machine learning algorithms that will constantly be analyzing traffic patterns, weather conditions, and other factors. It ensures fleets cut down fuel consumption, shorten delivery times and ultimately enhance overall fleet operational efficacy.
With the inclusion of AI & ML to FMS there would be a much more proactive approach towards fleet management that is going to be both efficient as well as safe.
Electric and Autonomous Vehicles
Therefore, this will see fleet management systems change in line with the industry’s shift toward electric vehicles and autonomous vehicles.
- Autonomous Vehicle Management: But with the rise of AVs, fleet management will encounter new challenges and new opportunities. Autonomous vehicles will also need to integrate with FMS such that fleet coordination, maintenance monitoring and regulatory compliance are all supported. In addition, FMS will be needed to handle autonomous operations and keep driverless vehicles updated on status and location in real-time.
IoT and Big Data
Fleet management is likely to be most significantly affected by increasing Internet of Things and big data in the near future. While more devices are becoming “connected” via the Internet, fleet managers will receive, for the first time ever, an incredible volume of information in real time-from sources like vehicles, cargo, and even driver conditions-through their fleet management system.
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT-enabled devices will allow fleet managers to monitor all aspects of their fleet in real-time. This means not only the health of the vehicle and its location but also cargo temperature, humidity, and even the drivers’ physical condition during long drives.
This convergence of IoT and big data will lead to even smarter and more efficient fleet management solutions delivering a deeper sense of what’s going on in the business and freeing up businesses to make better, data driven decisions.
Conclusion:
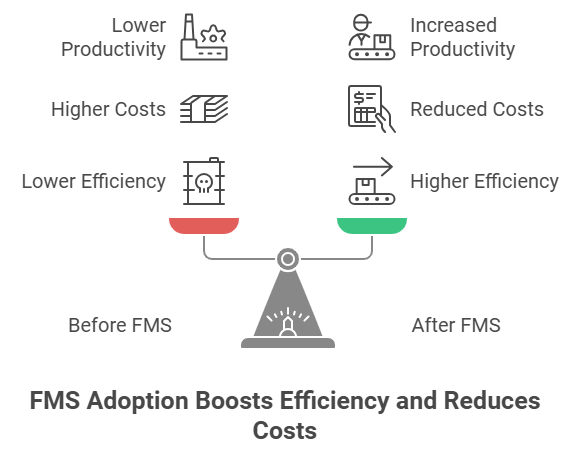
Recap: Efficiency, Cost Reduction and Safety
Fleet management software is actually designed to improve efficiency, reduce costs, ensure safety, and comply with applicable regulations. It allows businesses to optimize operations, save resources, enhance real-time tracking, and monitor maintenance and driver behavior.
Leading the Future
Today’s business, which embraces fleet management software, will be tomorrow’s industry leader. Be ready for the new technological environment in the future.
Evaluate Your Fleet Operations
This time is really to evaluate and finalize the implementation of FMS to keep competitive and increase the profitability of your fleet.
Contact Sigma Solve to find out about fleet management solutions that meet your needs.